Soluble TCR Expression & SPR Characterization Services
Service Features
SPR analysis of soluble TCR & Peptide-Ready MHC/Peptide-MHC interactions
SPR Characterization Services to Combat TCRs with Low Binding Affinity
TCRs often have low binding affinity to Peptide-MHCs (pMHC) which makes characterization via ELISA difficult. Alternatively, SPR is well suited for characterizing TCRS with low binding affinity. In addition to soluble TCR expression, we also offer SPR analysis services for characterizing the binding between TCRs and Peptide-MHCs or Peptide-Ready MHCs.
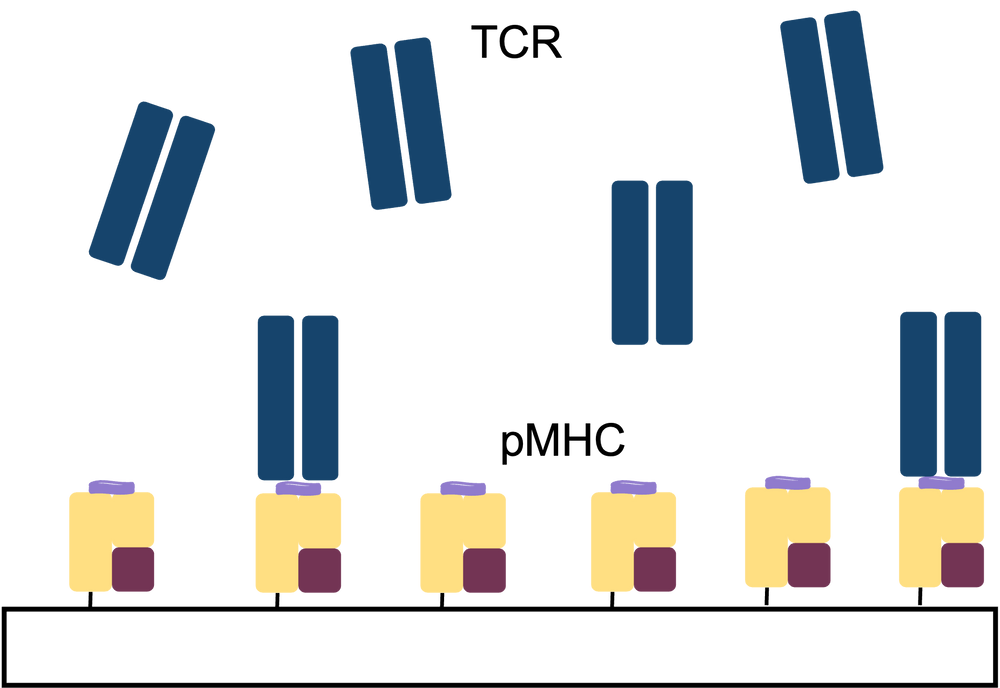
TCR Binding with Peptide-Ready MHC & Peptide-MHC
(A)
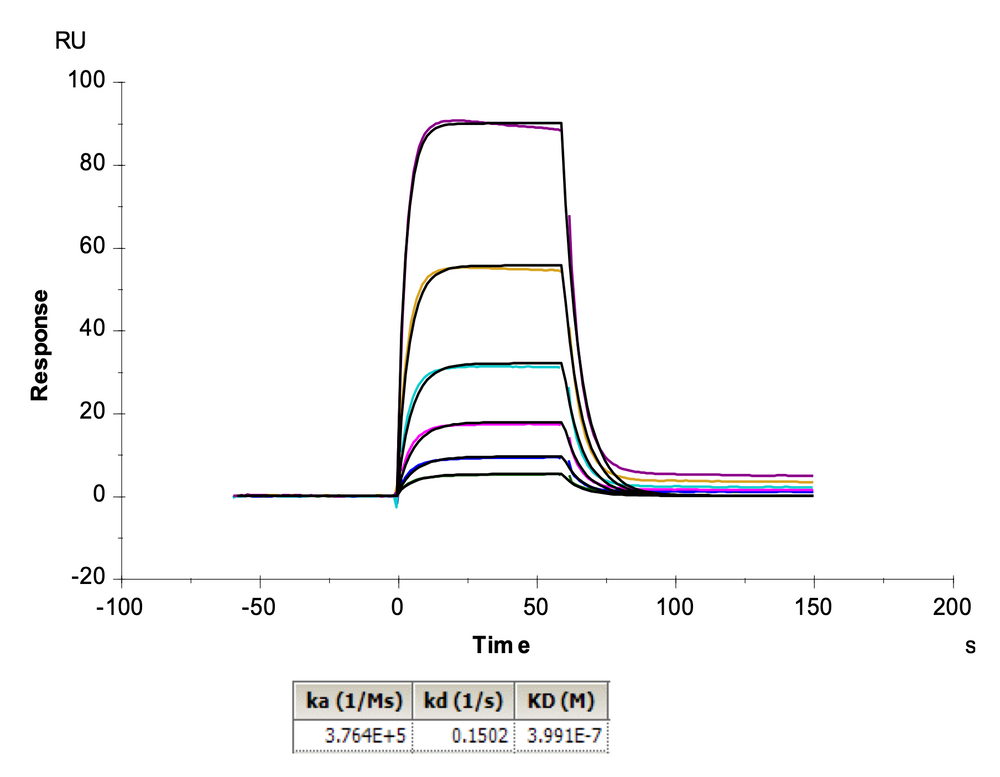
(B)
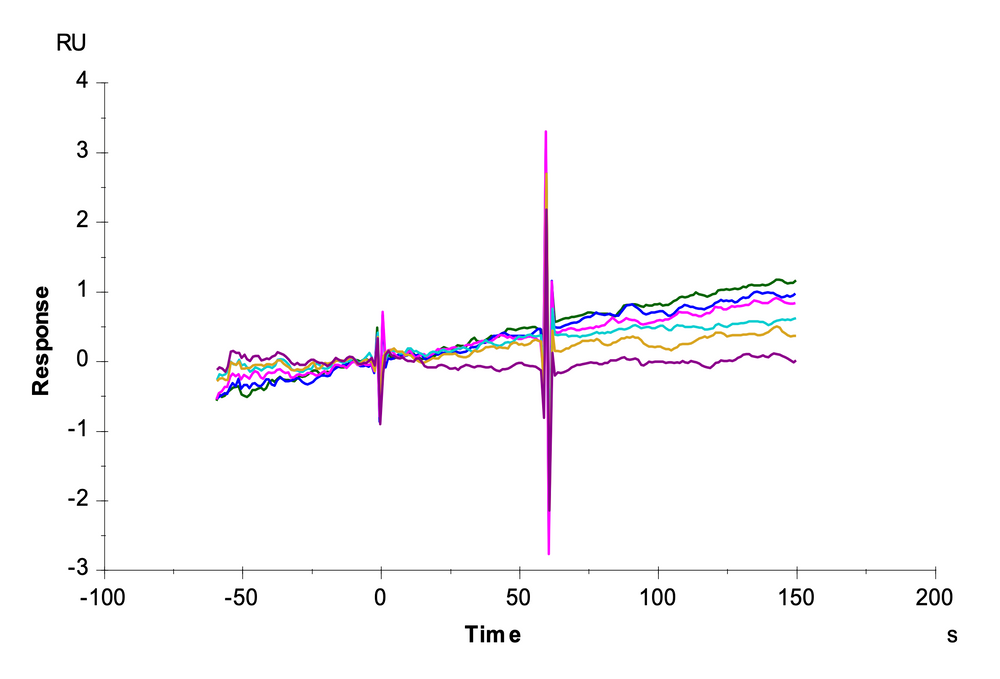
(C)
Figure 1. HLA-A*02:01 neoantigen loading efficiency in Peptide-Ready MHC loaded with FMNKFIYEI peptide (A), Peptide-MHC with FMNKFIYEI peptide (B), and MHC with no peptide (C).
Peptide-MHCs, Peptide-Ready MHCs, & Soluble TCR Expression
Get full support for your TCR therapy drug development endeavors with our comprehensive customized TCR and Peptide-MHC complex expression services.
Expression Validation: gp100 TCR & Anti-CD3 Bispecific Fusion Protein
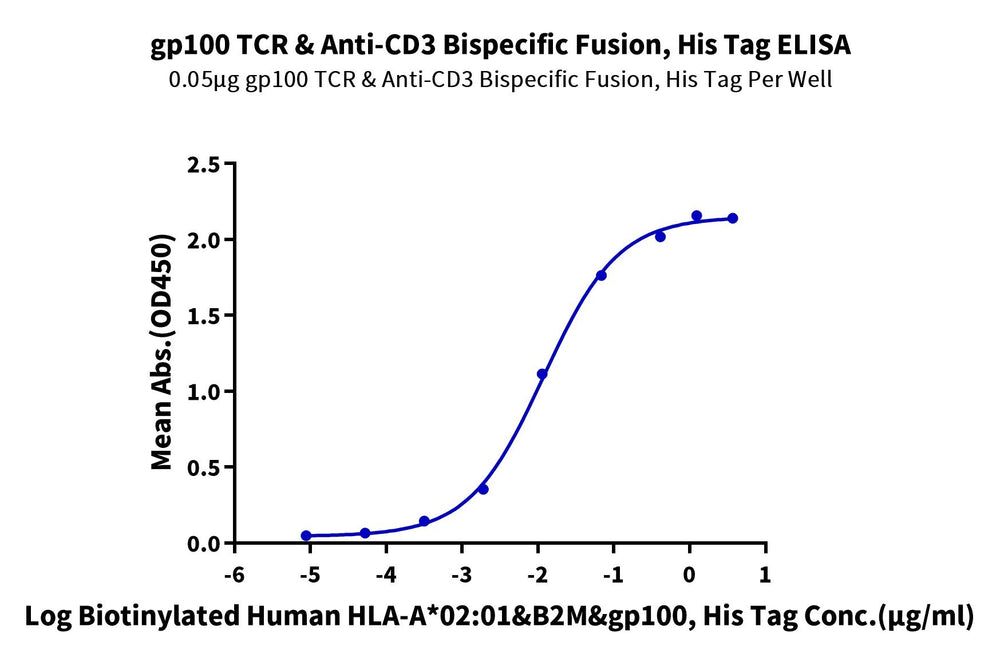
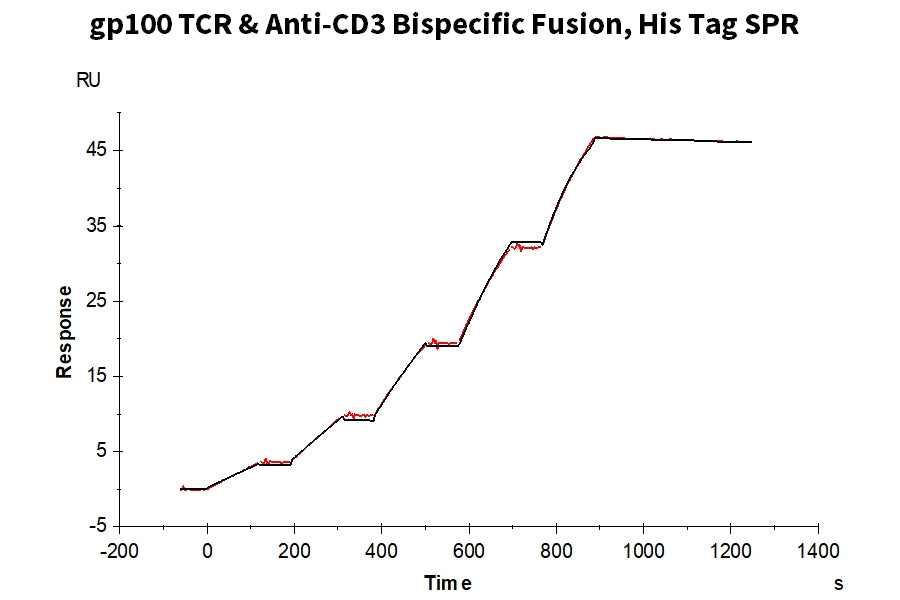
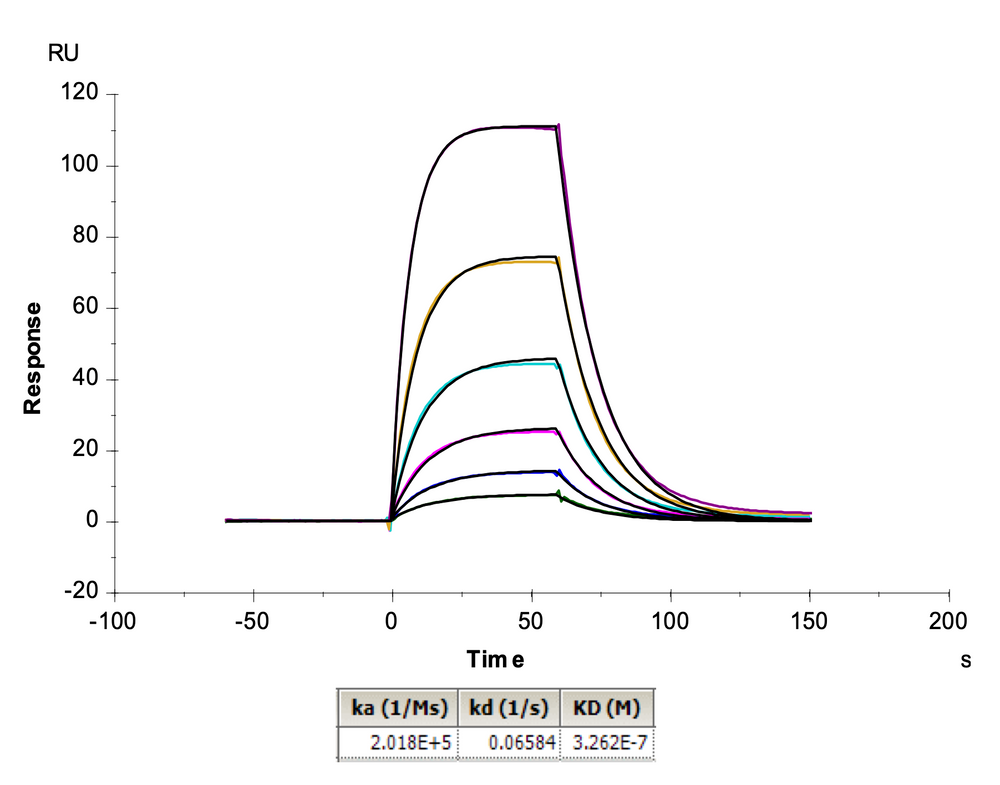
Figure 2. We have successfully expressed Tebentafusp, which not only binds to the GP100 (HLA-A*02:01) complex but also simultaneously binds to CD3 heterodimers, demonstrating excellent bidirectional binding activity. In ELISA (left) and SPR (right) analyses, Tebentafusp can bind to both monomers and tetramers of Human GP100 (HLA-A*02:01) complex, with an EC50 and affinity constant of 11.8 ng/mL and 0.196 nM, respectively.
About TCR Therapy
What is TCR Therapy?
TCR therapy is a novel immunotherapy developed based on the recognition pattern between the body's TCR and antigens. It includes two forms: T cell transfer therapy (TCR-T) and TCR protein drugs (TCR-scfv, TCR mimic antibodies, etc.). Among them, the principle of TCR-T involves first screening and validating TCR sequences that can recognize antigens. Through genetic engineering, these sequences are integrated into the patient's T cells, equipping them with the ability to selectively bind to and eliminate tumor cells expressing the target antigens. In this context, "antigen" refers to complexes formed by MHC (or HLA) with intracellular antigen peptides. Through this unique recognition mechanism, TCR-T can target a wider range of intracellular antigens, leading to more pronounced effects in solid tumors.
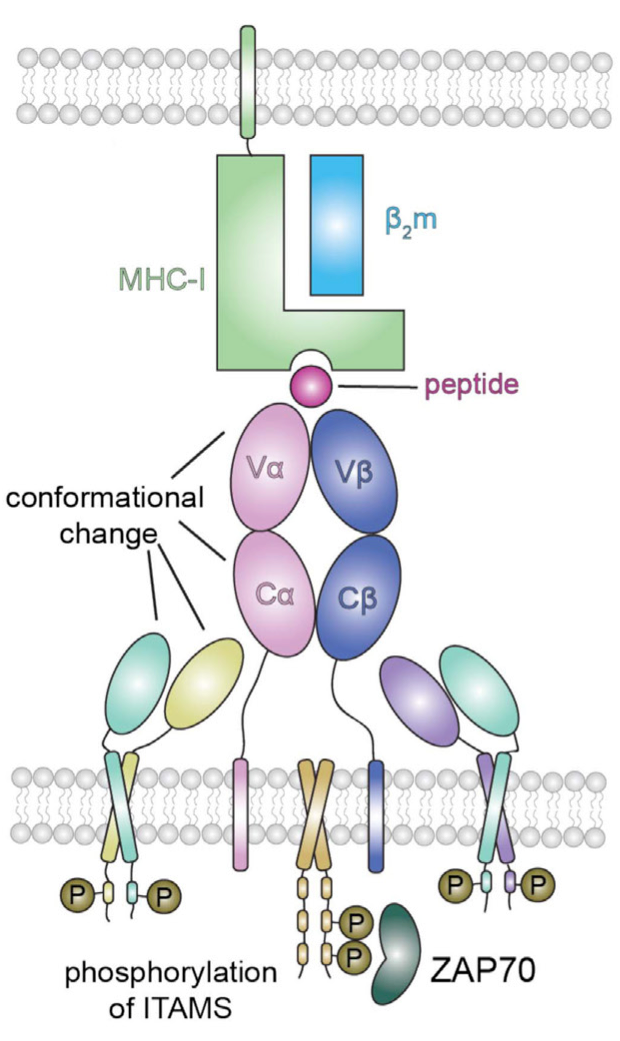
Figure 3. TCR Recognition of MHC-Peptide Complex [2]
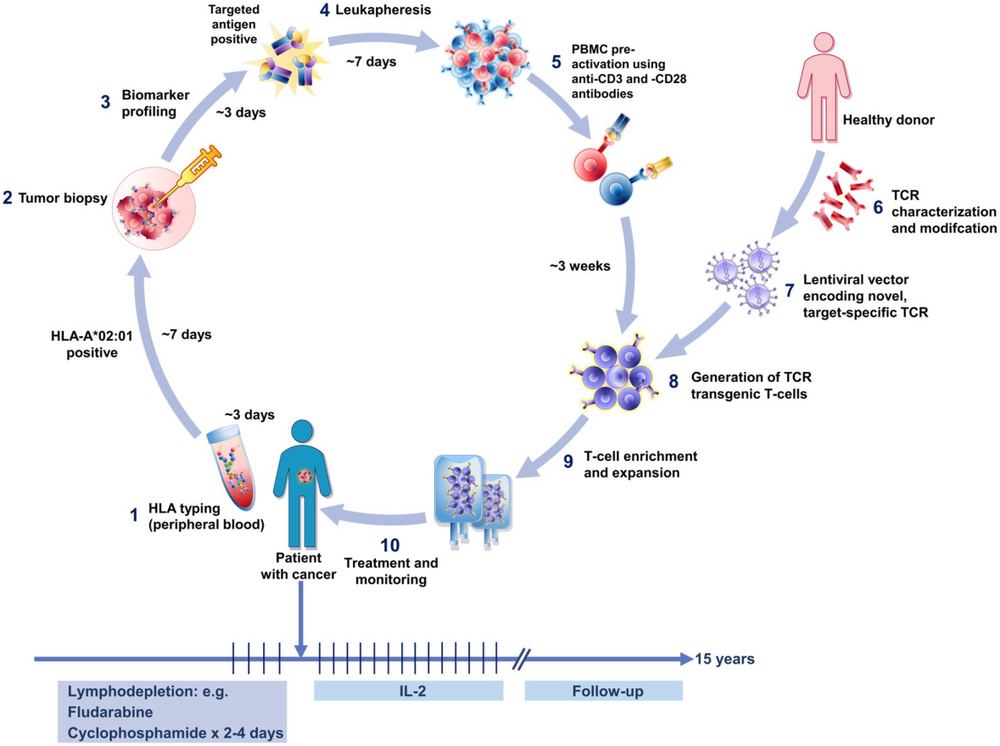
Figure 4. TCR-T Treatment Process [3]
Advantages of TCR Therapy
High specificity and sensitivity are prominent features of TCR-T therapy, especially in generating robust T cell responses against low-density antigen populations. Additionally, it exhibits a lower probability of cytokine release syndrome. Furthermore, compared to CAR, TCRs often possess lower affinity and faster dissociation, enabling continuous triggering of recognition responses and facilitating the amplification of immune signals.
TCR-scfv & TCR Mimic Antibodies
TCR-scfv (single chain variable fragment) and TCR mimic antibodies represent a novel class of protein engineering techniques, focusing directly on the development of protein drugs using TCR or TCR-like structures. This approach eliminates the need for genetic engineering and T cell transfer, resulting in a simpler manufacturing process and providing a more streamlined treatment option for clinical use. A representative drug in this category is Tebentafusp, currently the only approved TCR therapy on the market. It can simultaneously recognize the GP100 peptide-(HLA*02:01) complex and CD3.
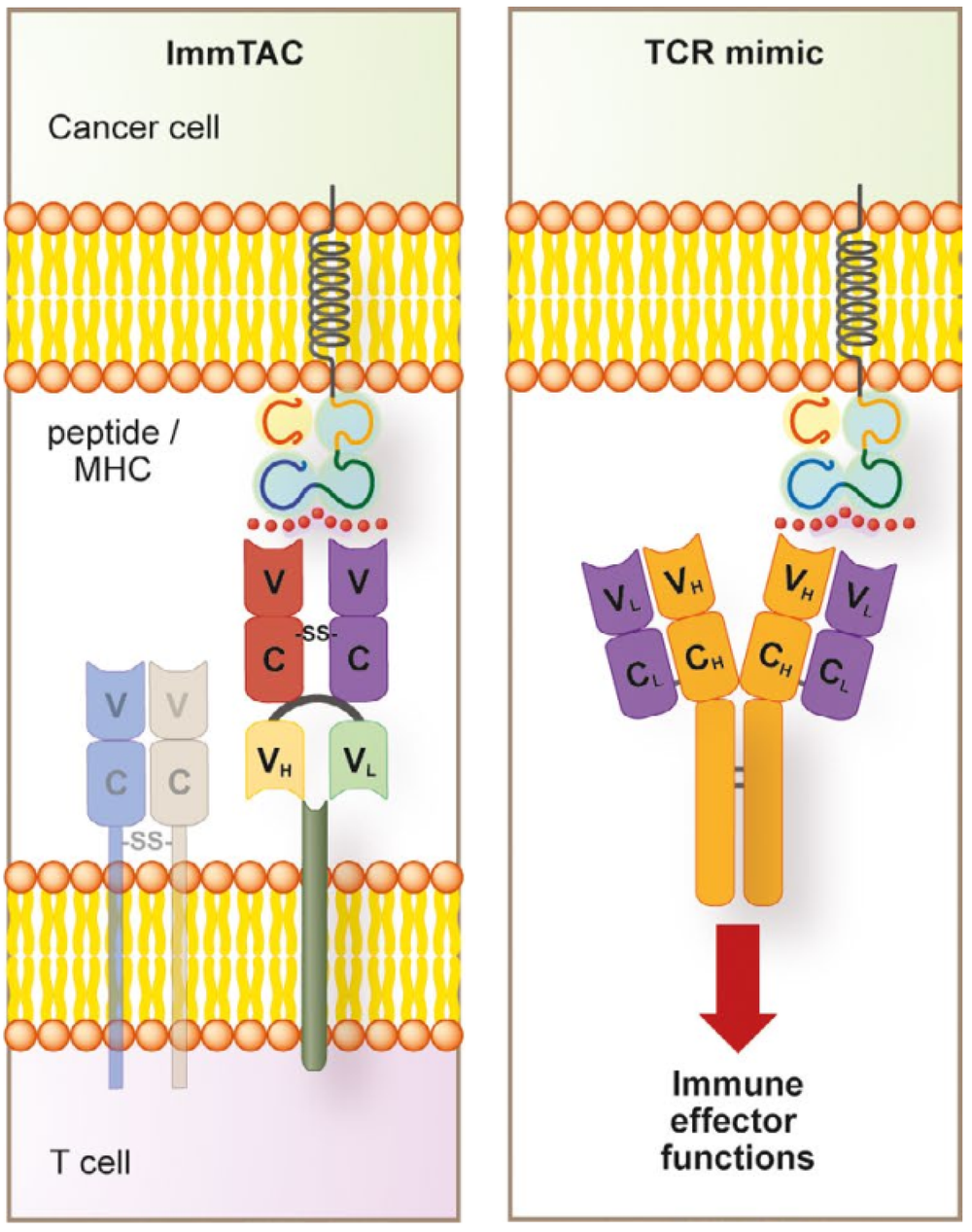
Figure 5. TCR-T Treatment Process [3]
References
[1] http://www.scgcell.com/
[2] Natarajan K, Jiang J, May NA, Mage MG, Boyd LF, McShan AC, Sgourakis NG, Bax A, Margulies DH. The Role of Molecular Flexibility in Antigen Presentation and T Cell Receptor-Mediated Signaling. Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 17;9:1657.
[3] Tsimberidou AM, Van Morris K, Vo HH, Eck S, Lin YF, Rivas JM, Andersson BS. T-cell receptor-based therapy: an innovative therapeutic approach for solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jun 30;14(1):102.
[4] Chandran SS, Klebanoff CA. T cell receptor-based cancer immunotherapy: Emerging efficacy and pathways of resistance. Immunol Rev. 2019 Jul;290(1):127-147.
TCR Therapy Solutions
Browse our solutions for TCR Therapy & request custom TCR / MHC services.